Sludge Handling in Wastewater Treatment
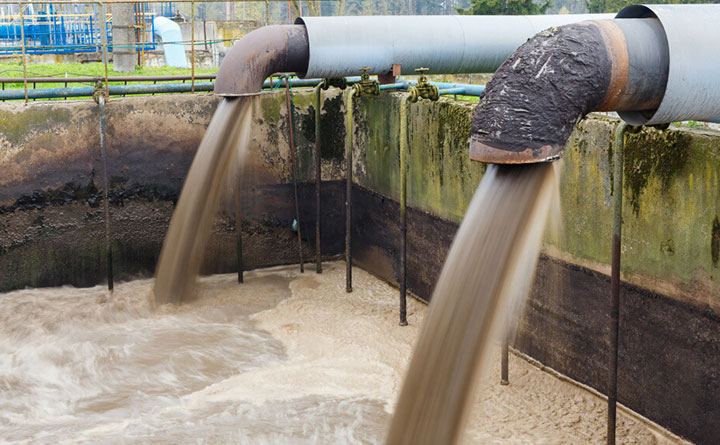
Sludge handling is a crucial part of wastewater treatment, focusing on the processing, treatment, and disposal of the solid byproducts generated during wastewater treatment. Proper sludge management ensures environmental protection, reduces health risks, and enables resource recovery.
Sludge is primarily classified into primary sludge, which consists of settleable solids from primary treatment, and secondary sludge, which comes from biological treatment processes. The handling process involves several stages, including thickening, stabilization, dewatering, and disposal or reuse.
Thickening – Reduces sludge volume by removing excess water, often using gravity thickeners or flotation units.
Stabilization – Treats sludge to reduce odors, pathogens, and organic content through aerobic or anaerobic digestion. Anaerobic digestion also produces biogas, which can be used for energy.
Dewatering – Further removes water using mechanical methods like centrifuges, belt filter presses, or drying beds, making sludge easier to handle.
Disposal or Reuse – Treated sludge can be disposed of in landfills, incinerated, or beneficially reused as fertilizer (biosolids) in agriculture.
With advancements in sludge treatment, resource recovery from sludge, including biogas production and nutrient recycling, is becoming a sustainable solution for wastewater treatment facilities, reducing waste and promoting environmental sustainability.