Separation and Filtration in Wastewater Treatment
Separation and filtration are essential processes in wastewater treatment, used to remove suspended solids, organic matter, and contaminants to improve water quality before discharge or reuse. These processes enhance the efficiency of biological and chemical treatments while ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
Separation Methods:
Sedimentation – Heavier particles settle at the bottom of tanks due to gravity, commonly used in primary treatment.
Flotation – Air bubbles help lift lighter particles, such as oils and grease, to the surface for removal.
Centrifugation – Uses centrifugal force to separate solids from liquids, often applied in sludge treatment.
Filtration Methods:
Sand Filtration – Removes fine suspended solids and microorganisms by passing wastewater through layers of sand and gravel.
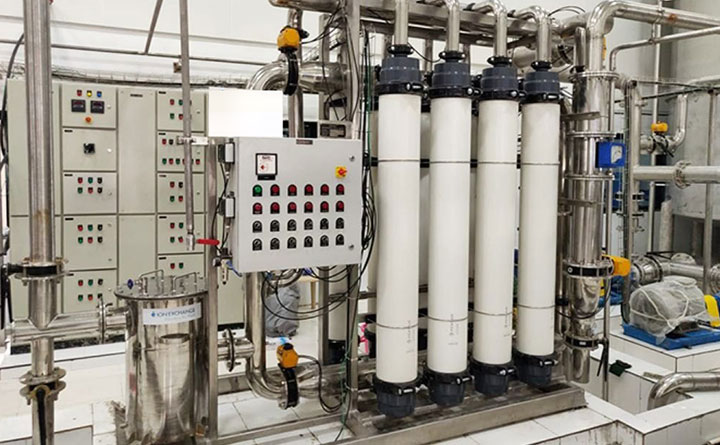
Membrane Filtration – Includes microfiltration, ultrafiltration, nanofiltration, and reverse osmosis, effectively removing bacteria, viruses, and dissolved contaminants.
Activated Carbon Filtration – Adsorbs organic pollutants, odors, and chemicals, improving water clarity and safety.
Separation and filtration play a vital role in wastewater recycling and reuse, ensuring clean and safe water for various applications, including irrigation, industrial processes, and even potable reuse in advanced treatment facilities.