Reverse Osmosis in Wastewater Treatment
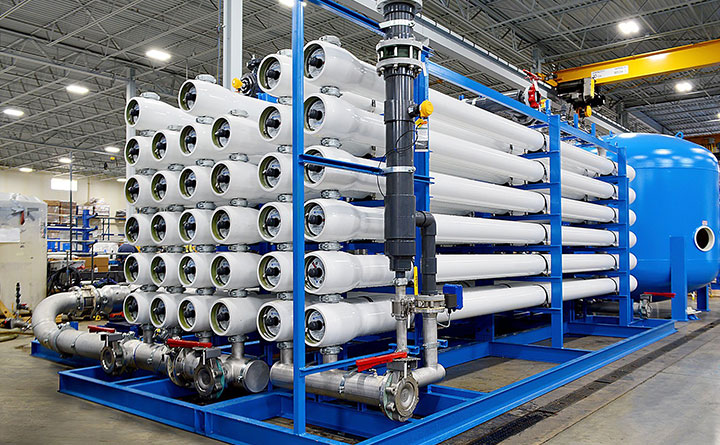
Reverse osmosis (RO) is an advanced filtration technology used in wastewater treatment to remove dissolved salts, contaminants, and impurities from water. It is widely used in industrial, municipal, and desalination applications to produce high-quality treated water for reuse or safe discharge.
RO works by applying pressure to force water through a semi-permeable membrane, allowing pure water to pass while blocking dissolved solids, heavy metals, bacteria, viruses, and other pollutants. The membrane has microscopic pores that are small enough to remove up to 99% of contaminants, making RO one of the most effective water purification methods.
Key Applications of RO in Wastewater Treatment:
Water Reuse and Recycling – RO-treated water can be reused in industrial processes, irrigation, and even drinking water in advanced treatment plants.
Desalination – Removes salt from seawater or brackish water, providing fresh water for regions with water scarcity.
Industrial Wastewater Treatment – Purifies wastewater from industries such as pharmaceuticals, food processing, and electronics manufacturing.
RO enhances sustainability by reducing wastewater discharge and conserving freshwater resources. However, it requires energy for operation and produces a concentrated waste stream (brine) that needs proper disposal. Advances in membrane technology continue to improve efficiency and reduce operational costs.